Prevention of Illegal Working Guide 2023
Understanding Employment Regulations: Navigating Legislation Against Illegal Working In the realm of regulations governing the prevention of illegal employment, it is strictly forbidden for employers to hire individuals who do not possess the Right to Work in the UK or those who violate the terms of their stay by engaging in work.
All businesses operating within the UK are legally obligated to adhere to the established framework aimed at curbing illegal employment. Neglecting these regulations can result in significant penalties, including substantial fines.
The concept of the ‘Right to Work’ holds immense importance in terms of immigration compliance and is relevant to every UK employer, regardless of their company’s size, industry, or whether they employ migrant workers. It is your responsibility to ensure that the Right to Work status of all individuals within your organization is confirmed before their employment commences. This entails conducting thorough and proper checks to verify their Right to Work.
Importantly, these regulations are applicable to employees of all nationalities and backgrounds, underscoring the need for fair and unbiased Right to Work checks, devoid of any discriminatory practices.

This guide offers comprehensive insights to employers about the framework for preventing illegal employment. It provides guidance on conducting valid Right to Work checks and clearly delineates the potential penalties that may be imposed should the Home Office identify any violation of your legal obligations.
What is the prevention of illegal working legislation?
Securing Legal Employment: Grasping the Idea of Preventing Unauthorized Work. The concept of “Prevention of illegal working” revolves around the duty placed upon employers to verify that any individual they hire has the legal authorization to work in the UK and fulfill the specific responsibilities linked to their role, as dictated by their immigration status.
This entails that employers have a responsibility to avert any form of unauthorized employment by conducting comprehensive right-to-work assessments for all potential employees before extending a job offer, irrespective of their claims of UK citizenship. Furthermore, this obligation also covers conducting checks on current employees whose work permission in the UK is restricted by time limitations.
What does prevention of illegal working mean for employers?
Legal Ramifications of Employment and Right to Work Verifications When an employer hires an individual whose immigration status prohibits them from legally working in the UK or carrying out specific job responsibilities, the employer exposes themselves to potential civil penalties and even the possibility of facing criminal prosecution.
Carrying out a valid and precise right-to-work check acts as a legal protection for employers. Even if it’s later discovered that an individual was working in violation of the law, a properly conducted right to work check can furnish the employer with a legal defense against civil liabilities. Conversely, if the mandated check is not executed accurately, the employer remains liable for ongoing civil penalties if any employee is found to be working without proper authorization.
The responsibility for conducting right-to-work checks squarely rests on the employer, even if this duty is delegated to staff members. It’s essential to emphasize that this responsibility cannot be delegated to a third party. While external assistance is permissible for technical support or specialized tools aimed at preventing illegal employment, relying on a recruitment agency, for example, cannot establish a legal defense.
As a result, in addition to setting up an internal process that aligns with compliance standards for verifying employees’ right to work, it is imperative to provide comprehensive training on right-to-work procedures to all individuals involved in your organization’s recruitment and onboarding protocols.
What Measures Should Employers Take to Comply with Regulations for Preventing Illegal Working?
Employers, along with any designated personnel responsible for overseeing recruitment and employment processes within the organization, need to possess a thorough understanding of their obligation to conduct right-to-work checks according to the established guidelines. This comprehension is crucial to ensure strict compliance with legal requirements.
In line with the framework for preventing illegal employment, it is paramount to consistently perform a right-to-work check before bringing an individual on board, thereby confirming their eligibility to assume the specific job role. Moreover, when an individual’s right to work is time-limited at the time of hiring, it is equally vital to conduct a subsequent check in proximity to the expiration of this authorization.
There are four distinct methods for conducting right-to-work checks, and the accurate execution of each of these methods serves as a legal defense mechanism, effectively protecting against potential civil liabilities.
Right to Work checks on EU workers
After the termination of EU freedom of movement and the implementation of the points-based immigration system, employers often have questions regarding the status and positions of EU workers.
EU citizens who were already living in the UK by December 31, 2020, have the option to continue their legal residence in the country. This is contingent upon them securing their status through the EU Settlement Scheme, which offers either settled or pre-settled status. The application deadline for this scheme was June 30, 2021. The verification of this status can be accomplished using a share code, combined with an online right-to-work check.
For EU nationals who arrived in the UK for employment purposes after January 1, 2021, the necessary step is to apply to the Home Office for a work visa. This visa, substantiated by appropriate documentation, must be presented during the right-to-work verification process.
Manual Right to Work checks
Three Key Stages of Manual Right to Work Checks:
- Acquiring Original Acceptable Documents: Obtain genuine copies of one or more acceptable documents from the potential or existing employees.
- Verifying Document Authenticity: Scrutinize the legitimacy of the provided document(s) while the holder is physically present.
- Copying and Document Record-Keeping: Create a clear copy of the document and ensure its accuracy. Also, document the date of the check and retain this record for future reference.
Classification of Acceptable Right to Work Documents:
The documents an individual can provide to confirm their Right to Work are grouped into two distinct lists: List A and List B.
Follow up Right to Work checks
Using Right to Work Check Results:
- List A Documents: Conducting an accurate Right to Work check with List A documents before employment establishes an ongoing legal defense for the individual’s Right to Work during their tenure. No additional checks are required while they are employed.
- List B Documents: If relying on List B documents, the defense is time-limited. To maintain immunity against civil liability, a follow-up check is necessary.
In both cases, it’s vital to verify the document’s authenticity and the individual’s identity. Keep clear, unalterable copies of documents securely for the individual’s employment duration and two more years. Include the check date in these records.
Online Right to Work checks
Exploring Online Right to Work Checks:
In certain instances, employers can conduct cost-free online assessments. The Home Office’s online checking service simplifies necessary checks, offering swift access to real-time migrant right-to-work details.
This approach enhances efficiency and security by reducing reliance on physical documents, which decreases the risk of forged documents and potential liabilities.
However, not all situations allow online checks. Feasibility depends on the individual’s eligibility for online verification, based on their immigration status. The online service currently supports assessments for non-EEA nationals with valid biometric residence permits/cards and EEA nationals under the EU Settlement Scheme.
To use the online service, employee consent is required. If an individual chooses not to use it despite compatibility, a manual check is recommended.
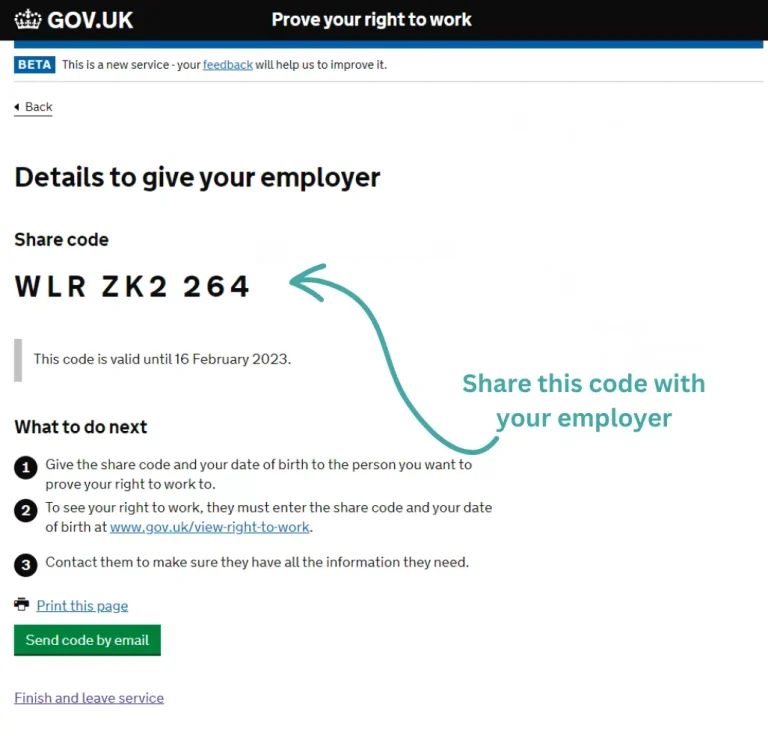
Functioning of the Online Service and Accessing ‘Share Codes’:
The online service gives individuals access to their Home Office right-to-work record. They generate a ‘share code’ from this platform, which contains necessary information.
Note that merely viewing the profile in the migrant section is insufficient. To establish a defense, use the dedicated employer section on the official government website.
The online Right to Work check involves three stages:
Utilizing Individual’s Right to Work Details:
- Access Details: Input the share code and individual’s date of birth to view their right to work information.
- Confirm Photo Identity: Verify that the displayed photo in the online check matches the individual presenting themselves.
- Keep Copy of Response: Retain a clear copy of the response provided by the online check service.
Retaining Right to Work Confirmation:
Ensure the profile page confirming an individual’s right to work, including their photo and check date, is securely kept. This page can be printed, saved as PDF, or in HTML format. Store it, electronically or in hard copy, during their employment and for two years after.
Important: If you hire someone after an online check, but it’s clear from the photo that the worker isn’t the same as in the check info, the risk of civil penalty for illegal work remains
Conclusion of COVID-Adjusted Right to Work Checks:
The temporary COVID-adjusted right to work scheme ended on September 30, 2022. During this scheme, remote Right to Work checks were allowed. Documents could be submitted as electronic copies, and verification was done via live video.
Employers aren’t required to redo checks for cases where COVID-adjusted checks were used. With the scheme closed, employers must now perform full document checks using one of the four specified methods.
What is the Employer Checking Service?
In certain cases, an individual may be unable to provide required documents, like when documents are held by the Home Office due to a pending application. In these situations, contacting the Home Office’s Employer Checking Service is crucial to establish a legal defense.
You’re required to request the Home Office to verify the immigration status of a potential or current employee under the following circumstances:
You must request the Home Office to verify the immigration status of a potential or current employee in the following scenarios:
- The individual can’t provide documents due to an ongoing Home Office appeal, review, or application.
- The individual has an Application Registration Card.
- The individual possesses a Certificate of Application issued within the last 6 months.
- The employee is a Commonwealth citizen who started residing in the UK prior to 1988.
In any of these situations, a legal defense can only be established if you obtain a Positive Verification Notice from the Home Office. This notice confirms that the individual is authorized to carry out the specific type of work in question.
New Right to Work rules from 6 April 2022
Starting April 2022, employers are obligated to perform online verifications for new employees with Biometric Residence Cards (BRCs), Biometric Residence Permits (BRPs), or Frontier Worker Permits (FWPs). Physical BRPs, BRCs, or FWPs will no longer be accepted as evidence for the right to work, even if they show a later expiration date.
Importantly, these changes won’t be applied retroactively to individuals employed on or before April 5, 2022, holding BRCs or BRPs. The previous document check requirements will remain applicable in these cases, ensuring compliance with prevention of illegal working regulations.
What are the penalties for breaching the rules?
If you breach the prevention of illegal working regulations, you may face a civil penalty of up to £20,000 for each unauthorized worker. Additionally, various additional consequences could follow:
- Disqualification as a director
- Seizure of earnings gained from illegal work
- Business closure with a court-issued compliance order
- Review and potential revocation of your sponsor license, impacting future migrant sponsorships to the UK
- Review and potential revocation of licenses in alcohol, late-night refreshment, and private hire vehicle/taxi sectors
If you are aware that you are hiring someone who isn’t permitted to perform the specific work, conducting a right-to-work check won’t provide you with a legal excuse against civil penalty liability.
If you knowingly employ an individual despite knowing or having reasonable cause to believe they lack the right to work, you also expose yourself to criminal prosecution. This offense can lead to imprisonment for up to 5 years and an unlimited fine.